Composite Geotextiles are multi-layered combinations of geosynthetic materials. Geocomposites are usually made from a UV resistant woven or non-woven fabric and a reinforced geogrid or polymer core to optimize performance and/or minimise cost.
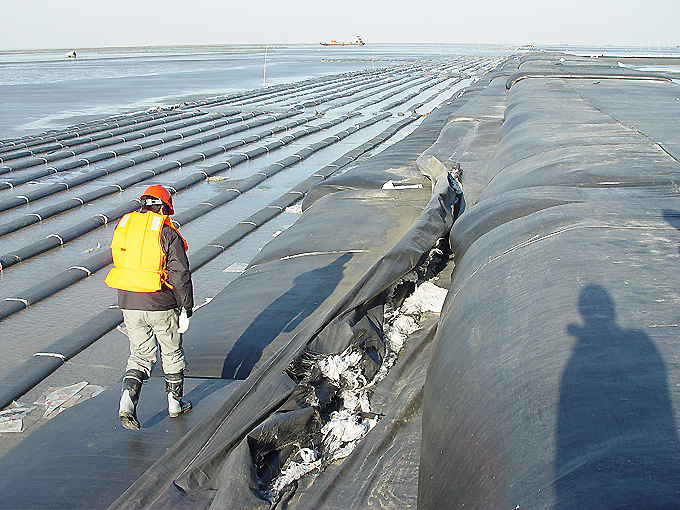

Geotubes filled with silt from dredging operations on the Yangste River
Geocomposites are regularly used in dewatering applications, to remove silt and control pollution from dredging operations, to intercept and remove leachates from landfill sites, and to transmit gases or water beneath pond liners.
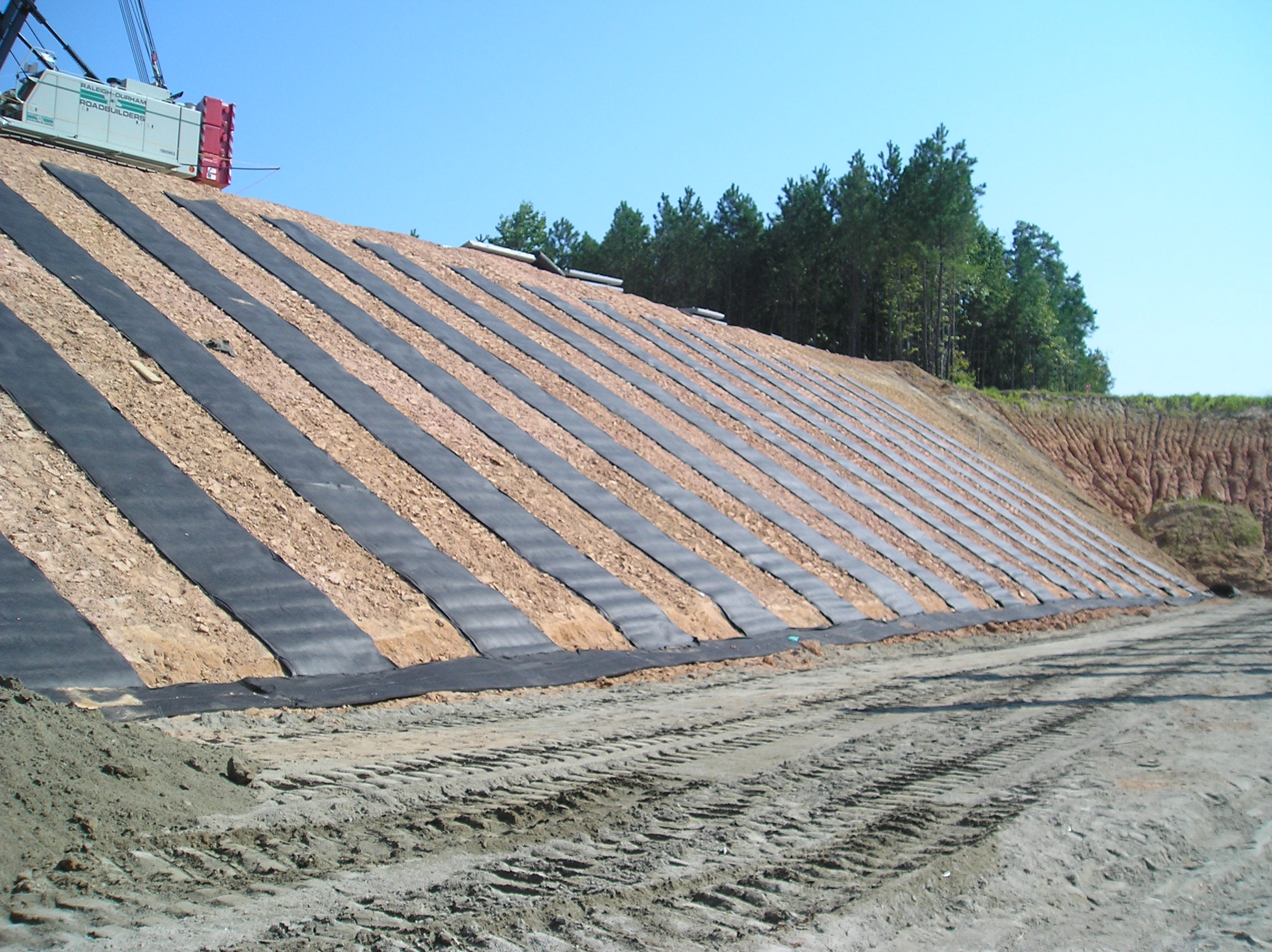

Geocomposite strip drains installed to remove seepage behind a shotcrete wall
Geotextile-polymer core composites, such as strip drains, allow very large quantities of liquid to flow inside a drainage core while a filter fabric prevents soil particles clogging the core. Because geocomposite drains are engineered to strict specifications, they overcome the extreme variation in permeability associated with sand and gravel traditionally used to control seepage.
Laminated composite geotextiles provide increased resistance to puncture, tear propagation, and friction related to sliding, as well as good tensile strength.
Applications for Composite Geotextiles:
- Composite geogrids for slope and wall reinforcement
- Strip and panel drains for pavement edge drains, shotcreting and construction.
- Sheet drains to protect geomembrane liners
- Reinforced silt barriers to contain silt runoff into streams
- Floating silt curtains to control pollution during dredging operations in low current and wave situations
- Geotextile dewatering bags for desludging wastewater ponds
- Geotubes for dredging operations where both high tensile strength and filtration properties are required
- Prefabricated vertical drains for dewatering applications.
Benefits of Composite Geotextiles:
- Enhanced functions
- Increased interface friction angles
- Increased speed of installation
- Superior separation, cushioning, reinforcement and drainage
- Floating silt curtains effectively control pollution during dredging operations