Biaxial Polypropylene Geogrids for soil reinforcement
Rigid biaxial geogrids improve the performance of aggregate base course materials supporting paved and unpaved roadway surfaces, railway ballast and Mechanically Stabilised Earth (MSE) walls and slopes. Their integrally formed structure provides lateral stability of unbounded base courses by the interlocking of granular particles into the geogrid apertures, thus improving their vertical stress distribution characteristics. The reinforcement action of polypropylene geogrids is generated by the vertical stress causing both the aggregate and geogrid to deform. Roads and railways built with PP biaxial geogrids have increased load bearing capacity, a longer service life and reduced section thickness.
Our biaxial geogrids are manufactured by extruding, punching, longitudinal and transverse stretching of polypropylene. This results in a geogrid with high flexural rigidity and high tensile modulus in both the longitudinal (MD) and transverse (TD) directions. Because polypropylene geogrids have excellent structural stability and strong mechanical interlock performance they are ideal for soil reinforcement.
The performance of unsealed and sealed roads is critically dependent on materials used. Research by the US Corps of Engineers has shown aggregate layers stabilised with PP geogrids deliver significant performance benefits to flexible road pavements and reduce surface rutting by up to 44% compared with non-stabilised aggregate. Incorporating geogrid into a road pavement could cut construction time and costs by up to 19% and delay the onset of pavement failure by controlling lateral and vertical displacement of aggregates from traffic loads. Geogrids also help to overcome shortages of quality quarried materials and natural gravels used for road construction.
Biaxial Geogrid Applications
- Base reinforcement – reduced lateral spreading of the base course
- Subgrade reinforcement – increased confinement leading to stiffer base
- Slope reinforcement
- Road pavements
- Mechanically Stabilised Earth embankment stabilization
Biaxial polypropylene geogrids are available with the following tensile strengths:
15/15kN/m 20/20kN/m 25/25kN/m 30/30kN/m 40/40kN/m 45/45kN/m 50/50kN/m
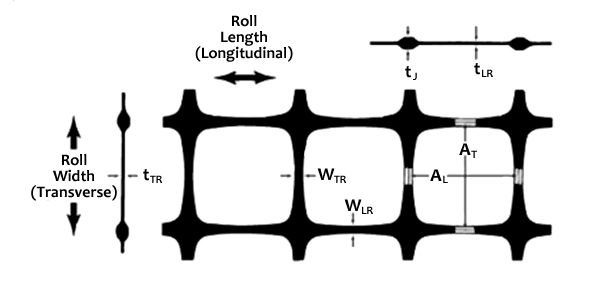
Structure of a composite biaxial geogrid
Specifications
| Product | AL | AT | WLR | WTR | tLR | tTR | tJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INFRAGRID1515 | 36 | 36 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 3.1 |
| INFRAGRID2020 | 35 | 35 | 2.6 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 1.1 | 3.5 |
| INFRAGRID2525 | 34 | 34 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 4.2 |
| INFRAGRID3030 | 34 | 34 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 4.9 |
| INFRAGRID4040 | 33 | 33 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.4 | 2.1 | 5.5 |
| INFRAGRID4545 | 32 | 32 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 5.6 |
| INFRAGRID5050 | 30 | 30 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 4.3 | 2.5 | 5.8 |
*unit=mm
Biaxial PP Geogrid INFRAGRID2020
| Index Properties | Test Method | Units | MD Values | TD Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | – | – | PP | – |
| Minimum Carbon Black | ASTM D 4218 | % | 2 | – |
| Tensile Strength @ 2% Strain | ASTM D 6637 | kN/m(lb/ft) | 7(480) | 7(480) |
| Tensile Strength @ 5% Strain | ASTM D 6637 | kN/m(lb/ft) | 14(960) | 14(960) |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | ASTM D 6637 | kN/m(lb/ft) | 20(1,370) | 20(1,370) |
| Strain @ Ultimate Strength | ASTM D 6637 | % | 13 | 13 |
| Structural Integrity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junction Efficiency | GRI GG2 | % | 93 | 93 |
| Flexural Rigidity | ASTM D 7748 | mg-cm | 750,000 | – |
| Aperture Stability | COE Method | m-N/deg | 0.50 | – |
| Dimensions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aperture Dimensions | – | mm(in) | 35(1.4) | 35(1.4) |
| Minimum Rib Thickness | ASTM D 1777 | mm(in) | 1.5(0.06) | 1.1(0.04) |
| Roll Width | – | m(ft) | 3.95(12.9) or 5.95(19.5) | – |
| Roll Length | – | m(ft) | 50(164) | – |